
Elfoid -- a REAL android phone
Robotics researchers from Osaka University have teamed up with NTT Docomo and Qualcomm to develop a handheld humanoid phone that brings a new dimension to mobile communications. A prototype of the device -- called "Elfoid P1" -- was unveiled at a presentation in Tokyo on March 3.

The Elfoid phone is a miniature version of the Telenoid R1 robot developed last year by a research team led by Osaka University professor Hiroshi Ishiguro. The current prototype measures 20 centimeters (8 in) long, is covered in a soft fleshy urethane skin, and has the same genderless and ageless appearance as the Telenoid. The control buttons are embedded in the chest, which glows green when the Elfoid is in use.

Dr. Ishiguro with Telenoid and Elfoid [Photo by: eSeL.at]
Like the full-sized Telenoid robot, the Elfoid handset is designed to add an element of realism to long-distance communication by recreating the physical presence of a remote user.

[Photo: Ars Electronica]
Equipped with a camera and motion-capture system, the Elfoid phone will be able to watch the user's face and transmit motion data to another Elfoid phone, which can then reproduce the face and head movements in real-time.

[Photo by: d_&_r]
The current prototype is unable to move, but future versions will incorporate tiny motors and parts made from shape-memory alloys, allowing the Elfoid to move its eyes, mouth, neck and arms. Other features will include a temperature sensor, accelerometer, and an easy-to-use voice and gesture based interface.

[Photo by: antjeverena]
The developers hope to have a fully operational Elfoid mobile phone within five years.
[Sources: ATR, Gizmodo Japan, Yomiuri]









 The high-precision BMI technology relies on three different types of brain activity measurements. EEG (electroencephalography) sensors measure the slight fluctuations in electrical potential on the scalp that occur when thinking, while NIRS (near-infrared spectroscopy) sensors measure changes in cerebral blood flow. Newly developed information extraction technology is used to process the complex data from these two types of sensors, resulting in a more accurate reading. The system reportedly has an accuracy rate of more than 90%.
The high-precision BMI technology relies on three different types of brain activity measurements. EEG (electroencephalography) sensors measure the slight fluctuations in electrical potential on the scalp that occur when thinking, while NIRS (near-infrared spectroscopy) sensors measure changes in cerebral blood flow. Newly developed information extraction technology is used to process the complex data from these two types of sensors, resulting in a more accurate reading. The system reportedly has an accuracy rate of more than 90%.
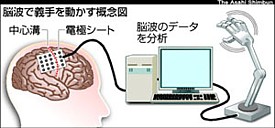 Researchers at Osaka University are stepping up efforts to develop robotic body parts controlled by thought, by placing electrode sheets directly on the surface of the brain. Led by Osaka University Medical School neurosurgery professor Toshiki Yoshimine, the research marks Japan's first foray into invasive (i.e. requiring open-skull surgery) brain-machine interface research on human test subjects. The aim of the research is to develop real-time mind-controlled robotic limbs for the disabled, according to an announcement made at an April 16 symposium in Aichi prefecture.
Researchers at Osaka University are stepping up efforts to develop robotic body parts controlled by thought, by placing electrode sheets directly on the surface of the brain. Led by Osaka University Medical School neurosurgery professor Toshiki Yoshimine, the research marks Japan's first foray into invasive (i.e. requiring open-skull surgery) brain-machine interface research on human test subjects. The aim of the research is to develop real-time mind-controlled robotic limbs for the disabled, according to an announcement made at an April 16 symposium in Aichi prefecture. 
 Whenever Robovie spotted people who looked disoriented, the child-sized droid wheeled up to them and asked, "Are you lost?" If so, the robot provided simple directions to the destination and pointed the way. If not, the robot proceeded to recommend nearby shops and restaurants.
Whenever Robovie spotted people who looked disoriented, the child-sized droid wheeled up to them and asked, "Are you lost?" If so, the robot provided simple directions to the destination and pointed the way. If not, the robot proceeded to recommend nearby shops and restaurants.